1、 Core structure and working principle
Core structure:
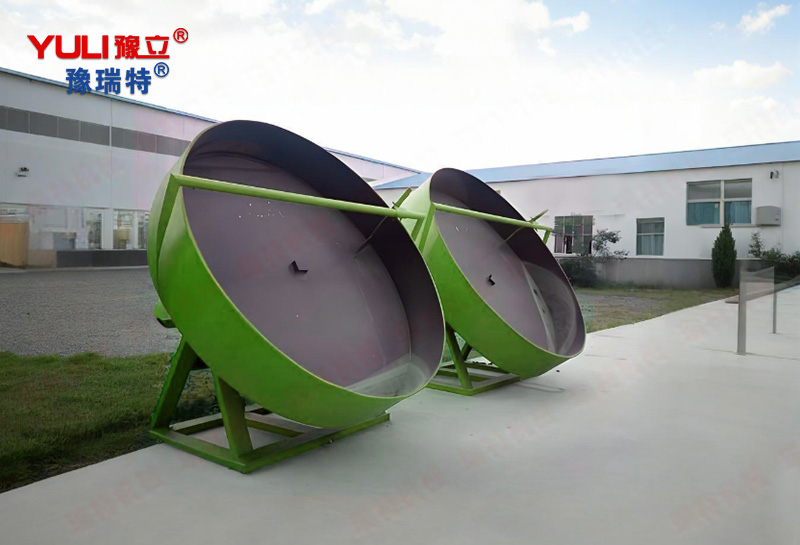
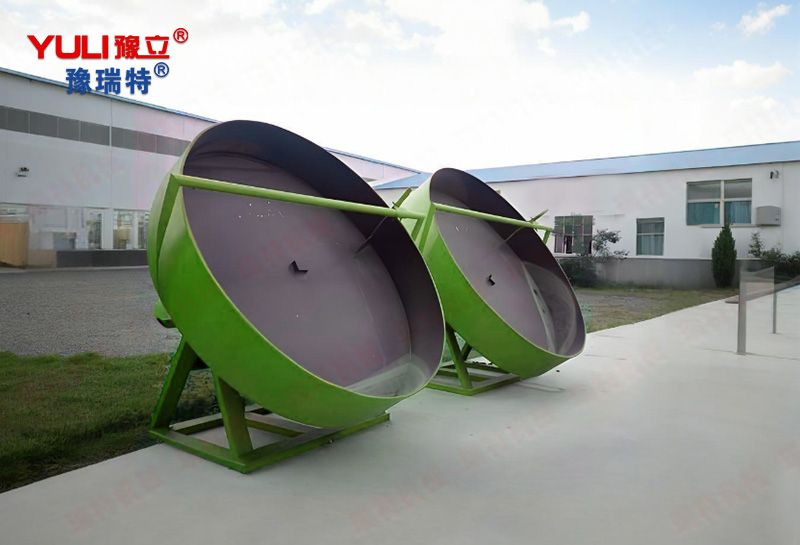
Tilting disk: It is the core component of the equipment. Usually made of
carbon steel, stainless steel, or lined with special
wear-resistant/corrosion-resistant materials. The disc is installed at a certain
angle (usually adjustable from 35 ° to 65 °) around its central axis.
Spindle and Base: A sturdy support and drive system that drives the disc to
rotate smoothly.
Scraper system: including bottom scraper and side scraper, used to prevent
material from adhering to the bottom and side walls of the disc, ensuring normal
granulation and unloading.
Spray system: located above the disc, it is used to evenly spray liquid
binder (water, solution, molten liquid, etc.) into the powder.
Rack, transmission device (motor, reducer), adjustment mechanism (used to
adjust tilt angle), and protective cover, etc.
Working principle ("snowball" rolling and sticking principle):
The process is very intuitive, similar to rolling a snowball:
Feeding: The powdered or fine granular raw materials to be granulated are
continuously or batched into a rotating inclined disc.
Wetting: the spray system evenly sprays the liquid binder on the tumbling
bed.
Nucleation: Under the capillary force of liquid and the rolling and
friction generated by disk rotation, fine powders adhere to each other, forming
a large number of tiny initial particles ("mother balls" or "nuclei").
Growth: As the disk continues to rotate, these small particles adhere to
the surrounding fine powder and aggregate with each other in a complex motion
trajectory (rolling, sliding, throwing), gradually growing like snowballs.
Graded discharge: Due to different particle sizes, the equilibrium points
of gravity and centrifugal force are different. When the particles grow large
enough, they will overcome centrifugal force and move upwards, eventually
reaching the edge of the disk and overflowing and being discharged. Smaller
particles remain in the disc and continue to grow, achieving "natural grading",
which is a unique advantage of the disc granulator.
Finished product: The discharged particles enter downstream processes such
as drying and screening.
2、 Main features
Advantages:
High ball formation rate and uniform particle size: The natural grading
effect ensures the uniformity of the discharged particles.
Good particle strength: The particles formed by layer by layer rolling and
bonding have a dense structure and high strength.
Intuitive and flexible operation: Operators can directly observe the
formation of balls in the disc and adjust parameters such as tilt angle, speed,
and spray volume in real time to quickly change product particle size, with
strong flexibility.
Simple structure, easy maintenance: no complex moving parts, low failure
rate, easy to clean and repair.
Low investment and operating costs: Compared to some pressure granulation
equipment such as rollers and tablet presses, its cost and energy consumption
are usually lower.
Can handle a variety of materials: suitable for materials with moderate
heat sensitivity and viscosity.
Disadvantages/Limitations:
Single machine production capacity is relatively limited: for production
lines with large output, multiple units may need to be connected in
parallel.
High requirements for dust control: The rolling process of dry powder will
generate dust, requiring a good ventilation and dust removal system.
Sensitive to material characteristics: The adhesion, humidity, particle
size distribution, and other factors of the material have a significant impact
on ball formation, and sometimes it is necessary to add binders or adjust the
formula.
Particle shape and density: Irregular spherical (quasi spherical) particles
are usually produced, and the particle density is usually lower than that of
high-pressure methods such as extrusion granulation.
3、 Key operating parameters and adjustments
Disk inclination angle: affects the residence time and rolling speed of
materials inside the disk. The larger the angle, the shorter the residence time,
and the smaller the particles; On the contrary, the larger the particles.
Disk speed: affects the motion state and centrifugal force of the material.
The rotation speed is too high, and the particles are thrown up and difficult to
form; Too low, insufficient particle rolling. It needs to be adjusted in
conjunction with the tilt angle.
Spray volume and position: The spray volume directly affects the ball
formation rate and particle size. Uniform and well atomized. The nozzle position
is usually located above the "ball forming area".
Raw material characteristics: including particle size, moisture content,
adhesion, etc.
Scraper position: Ensure that the bottom and sides of the disc are clean
and maintain normal material movement.
4、 Main application areas
Fertilizer industry: the main equipment for granulation of compound
fertilizers, organic fertilizers, and BB fertilizers.
Metallurgical industry: chunking (pellet) of iron ore powder and
non-ferrous metal ore powder for use in blast furnaces or direct reduction.
Building materials industry: ball forming of cement raw materials,
refractory materials, and ceramic blanks.
Environmental protection industry: Solids solid waste such as dust, sludge,
and fly ash into balls for easy transportation, disposal, or resource
utilization.
Chemical industry: granulation of various chemical powder raw materials
(such as pigments, catalyst precursors, inorganic salts, etc.).
Feed industry: producing pellet feed.
5、 Comparison with other common granulators
| 特性 | 圆盘造粒机 | 转鼓造粒机 | 对辊挤压造粒机 | 流化床造粒机 | 喷雾造粒塔 |
|---|
| 原理 | 滚动团聚 | 滚动团聚 | 机械挤压 | 流化喷涂团聚 | 雾化干燥 |
| 颗粒形状 | 不规则球形 | 不规则球形 | 圆柱形、枕形 | 多孔球形 | 实心球形 |
| 颗粒强度 | 中高 | 中高 | 很高 | 中低 | 中 |
| 灵活性 | 很高 | 中 | 低(需换模具) | 中 | 低 |
| 产能 | 中 | 大 | 大 | 中 | 很大 |
| 主要应用 | 肥料、冶金、建材 | 肥料(尤其大规模) | 医药、化工、肥料 | 医药、食品、化工 | 化工、陶瓷、奶粉 |