Introduction to Pig Manure Organic Fertilizer Equipment
2026-01-28
The unique features of pig manure: Pig manure has a finer texture and
contains more organic matter and nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and
potassium. It decomposes slowly and is suitable as a base fertilizer. One pig's
manure can increase grain production by 200-300 pounds. 1. Organic fertilizers
contain a type of organism and enzyme that can enhance the soil's biological
properties and enzyme activity, increase soil nutrients, and improve soil
acidity and alkalinity, making the soil suitable for various agricultural
growth. 2. The organic fertilizer produced has strong nutritional value. If
evenly distributed, it can last for at least 100 days without the need for
additional fertilizers. This effect cannot be replaced by any fertilizer. 3.
Organic fertilizers can be added with anti pest drugs during production to
reduce diseases, pests, and rodent infestations. 4. The organic fertilizer
produced is nutrient rich and contains not only nitrogen, phosphorus, and
potassium, but also abundant calcium, magnesium, and silicon, which can alter
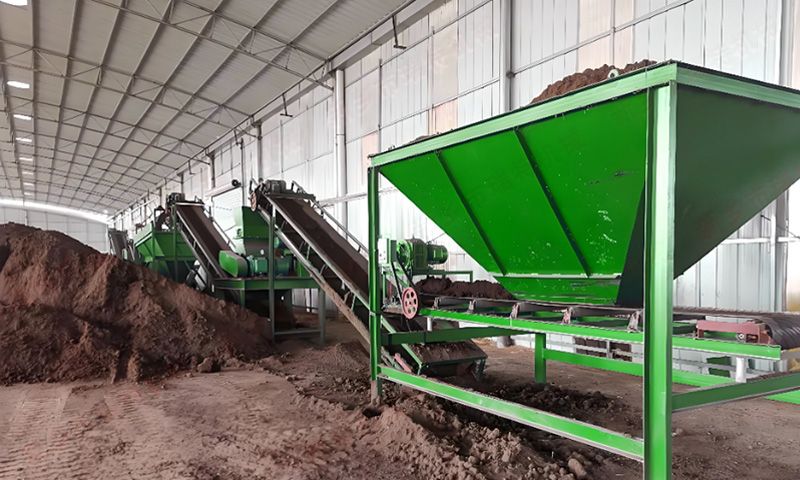
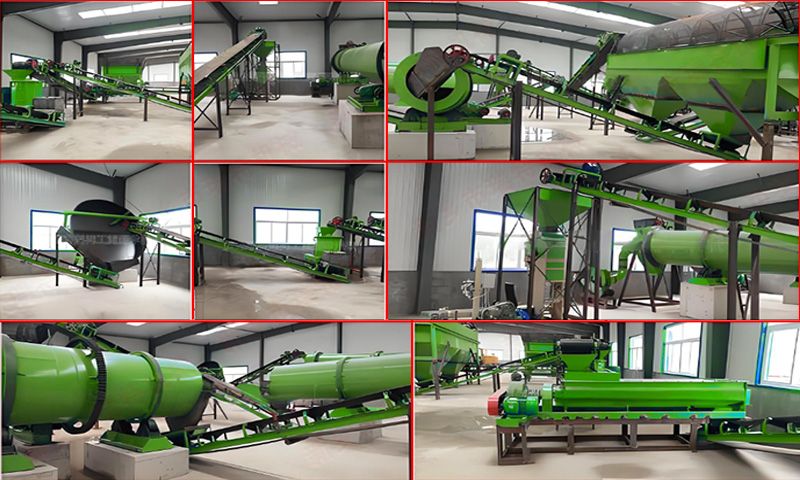
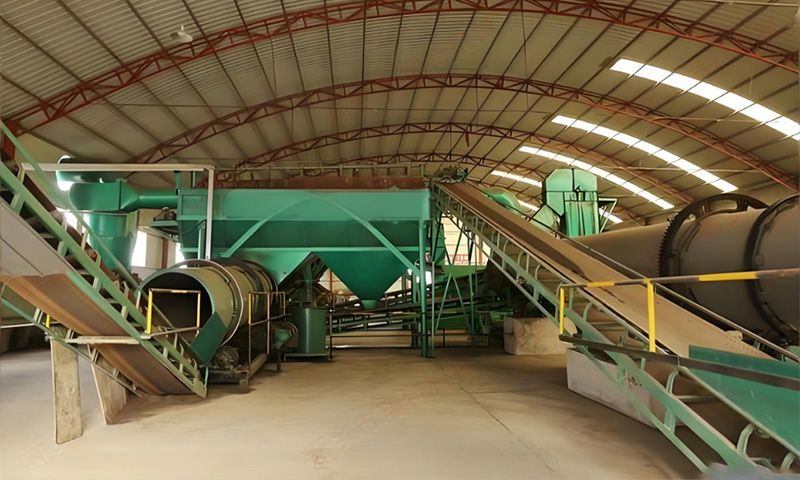
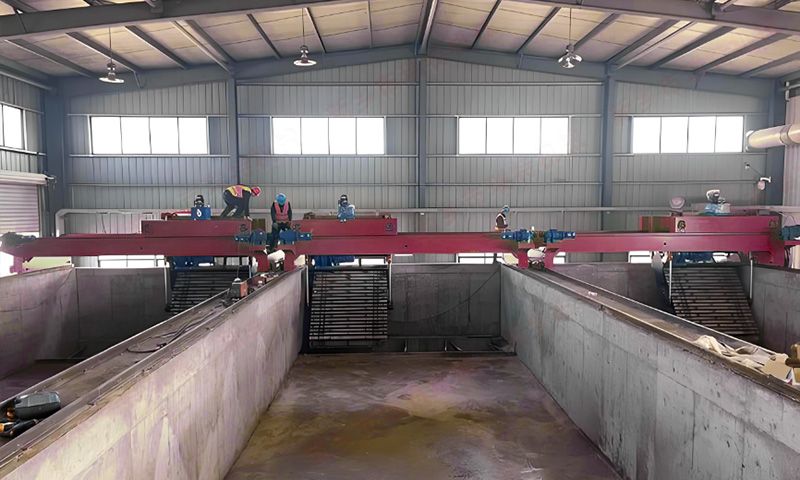
soil composition and promote crop growth. Using a pig manure organic fertilizer production line to process commercial
organic fertilizers requires three steps: pre fermentation, deep processing and
powder production, and deep processing and granulation. The pig manure organic
fertilizer production line is a series of production equipment that uses pig
manure as raw material, undergoes high-tech equipment fermentation and
processing, and produces organic fertilizer. It is equipped with fermentation
turntables, organic fertilizer crushers, drum screening machines, horizontal
mixers, organic fertilizer granulators, rotary dryers, coolers, screening
machines, coating machines, packaging machines, conveyors and other
equipment. The process flow of the pig manure organic fertilizer production line is as
follows: ① Raw material fermentation - ② Automatic raw material batching system - ③
Crushing and mixing - ④ Organic fertilizer granulation, drum granulation,
extrusion granulation - ⑤ Drying machine for organic fertilizer granules - ⑥
Cooling machine for organic fertilizer granules - ⑦ Screening machine for
qualified organic fertilizer granules - ⑦ Intelligent small-scale fertilizer
mixing equipment | Intelligent small-scale organic fertilizer production line -
⑧ Coating machine for smoother coating granules - ⑨ Packaging scale for
automatic filling of organic fertilizer granules - ⑩ Sealing Introduction to the Process Flow of Pig Manure Organic Fertilizer
Production Line Early stage pig manure fermentation section: Directly feed the recycled livestock and poultry manure into the
fermentation area. After one fermentation and two aging stacking, the odor of
livestock and poultry manure is eliminated. At this stage, fermentation strains
can be added to decompose the coarse fibers, so that the particle size after
crushing meets the particle size requirements of granulation production. 1. Fermentation equipment a. Trough aerobic fermentation: This is currently an effective method for
treating pig manure and is also suitable for the commercial production of pig
manure organic fertilizers, which is conducive to standardized production. It
utilizes biological characteristics combined with mechanized technology, using
natural microorganisms or inoculated microorganisms to completely decompose pig
manure and convert organic matter into organic matter, carbon dioxide, and
water. This method has a short fermentation time, usually about 15 days, and is
easy to achieve factory scale production. It is not affected by weather seasons
and causes minimal pollution to the environment, which is conducive to the
commercial production of pig manure organic fertilizer. Depending on the
equipment, the width of the fermentation tank is generally 3-20m, the depth is
generally 0.8-1.5m, and the length is 50-100m, which can be designed according
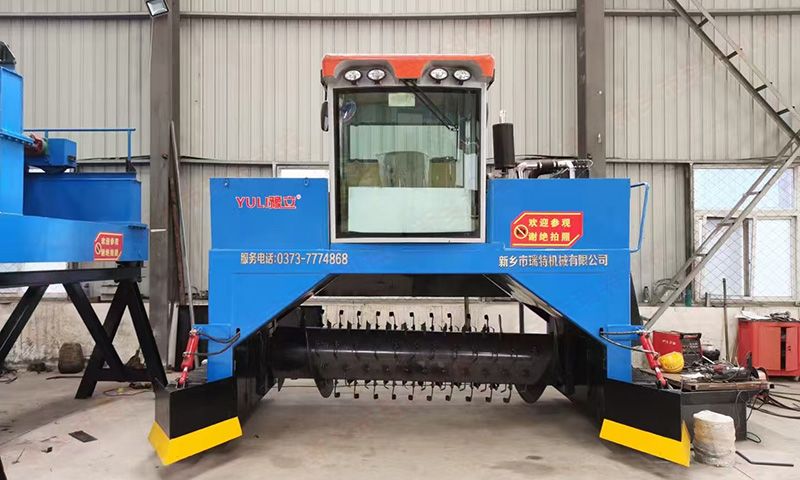
to the actual situation. b. Strip composting is the process of stacking a mixture of raw materials
into long, strip-shaped piles or stacks, and maintaining an aerobic state in the
pile through regular manual or mechanical turning and natural ventilation.
Fermentation and decomposition are carried out under aerobic conditions. The
cross-section of the stack can be trapezoidal, irregular quadrilateral, or
triangular. Stacking composting fermentation is the process of spreading
materials into rows and stacking them outdoors or under a shed. Each row of
materials is 2-3 meters wide and 1-1.5 meters high, with the length depending on
the actual situation. Ventilation pipes can be installed under the material
pile, or ventilation facilities can be omitted. The characteristic of using
stack composting to treat pig manure is that the materials can be placed close
to the farmland, without the need for dedicated factories, but the processing
time is relatively long. If the outdoor method is used, it is greatly affected
by the weather season. c. The closed high-temperature fermentation equipment for organic
fertilizer of livestock and poultry manure can transfer manure with a moisture
content of up to 80% to a fermentation tank through a conveyor belt. After
high-temperature and aerobic fermentation, it can be directly processed to about
30% safe storage moisture in one go. The entire process is completed in the
fermentation tank without odor pollution, thereby reducing environmental
pollution during the drying process and meeting national environmental
protection standards. 2 Precautions during Fermentation Process a. Raw material particle size: The particle size of pig manure and
auxiliary materials should be below 10mm, otherwise they need to be crushed; b. Suitable material moisture: Composting microorganisms are more suitable
for fermentation humidity of 50-60%, and high humidity of 60-65%, so the
material moisture should be adjusted to around 55-60%. When the moisture content
reaches 65% or more, there is a higher chance of dead tanks not fermenting. c. Control of pig manure and auxiliary materials: According to local
agricultural conditions, organic materials such as straw, corn stalks, peanut
stems, etc. can be used as auxiliary materials. The ratio of pig manure to
auxiliary materials can be adjusted according to the requirements of
fermentation moisture. (Generally 3:1), composting materials can be selected
with a carbon to nitrogen ratio of 20-80:1. So common organic materials in rural
areas, such as dry straw, corn stalks, fallen leaves, soybean stems, peanut
stems, etc., can be used as auxiliary materials for composting fermentation
after being crushed. d. Fermentation cycle: After mixing pig manure, auxiliary materials, and
inoculation materials in the tank, they are flipped once, which is recorded as
the start time of the fermentation cycle. Generally, after a 3-4 day heating
period (5-7 days in winter), they enter the high-temperature fermentation stage.
Based on temperature, when the temperature of the pile exceeds 60-70 ℃ and is
maintained for more than 24 hours, the pile can be flipped, and the number of
flips varies with the season. The fermentation cycle in summer is generally 15
days, and in winter it is 25 days. If the temperature inside the fermentation tank does not exceed 40 ℃ after
entering the tank for 10 days, it can be determined as a dead tank and the
fermentation start-up fails. At this point, it is necessary to measure the
moisture content in the tank. If the moisture content exceeds 60%, auxiliary
materials and inoculation materials need to be added; If the moisture content is
below 60%, consider whether the amount of inoculum material added is
insufficient. Deep processing powder production The fermented material needs to be crushed in a grinder, and after
processing, the finished product is screened out by a screening machine to
remove impurities Deep processing granulation 1. After crushing and screening, the material enters the mixing and
stirring system. Before mixing and stirring, according to the formula, N, P, K,
and other trace elements are added to the mixing and stirring system to start
stirring and stir evenly to achieve a uniform fertilizer efficiency content of
the entire fertilizer particles. 2. Transport the mixed materials into the granulation system (a rotary drum
granulator or an extrusion granulator can be used). 3. Particle drying: Send the particles made by the granulator into the
dryer to dry the moisture contained in the particles, increase their strength,
and facilitate storage. 4. Particle cooling: The dried fertilizer particles have a high temperature
and are prone to clumping. After cooling, they are easy to store in bags and
transport. 5. Particle classification: The cooled particles are classified, and those
that do not meet the requirements are crushed by a crusher and returned to the
granulation system for further granulation. Screen out qualified products. 6. Finished product coating: Coat qualified products with coating to
increase the brightness and roundness of particles. 7. Finished product packaging: The finished particles are bagged by an
automatic packaging machine and stored in the warehouse